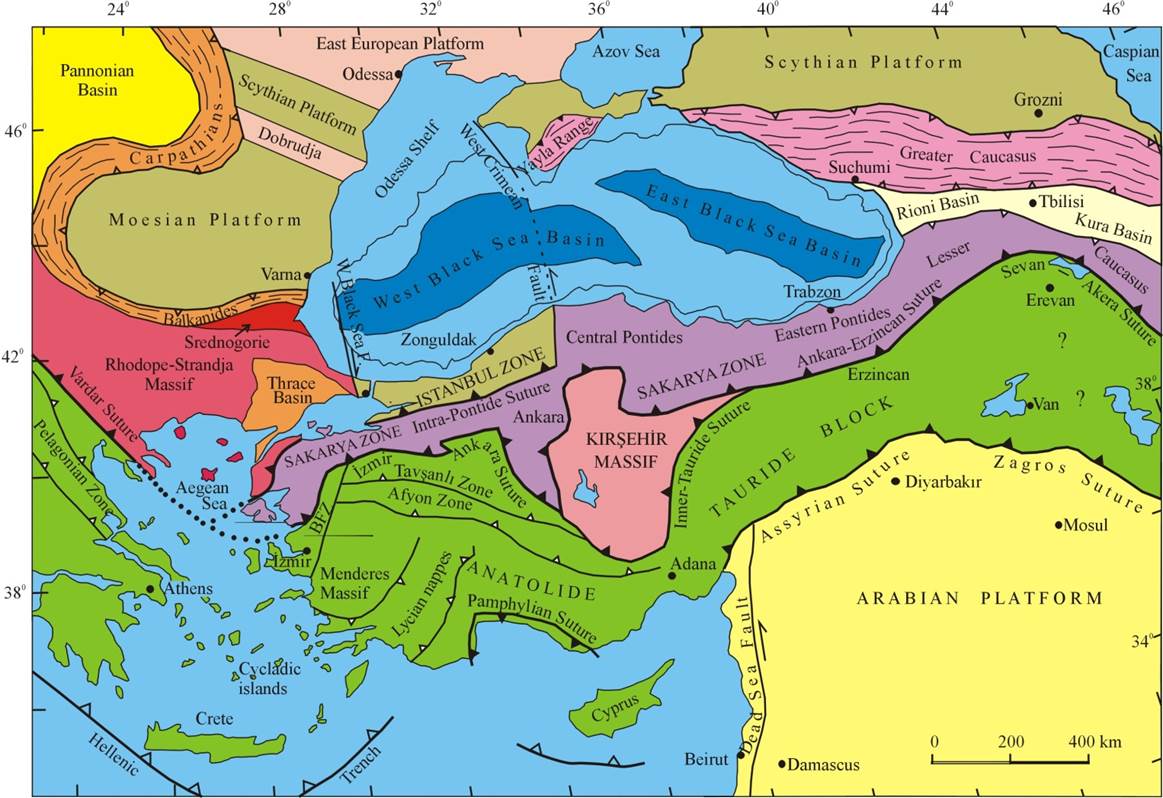
The publications are arranged thematically in the
following order
(consult the map above for the location of the
respective tectonic zone):
TECTONICS OF TURKEY
General tectonics of Turkey
Paleotethyan
evolution of the eastern Mediterranean
Neotethyan evolution
of the eastern Mediterranean
Pontides
Sakarya Zone western part
- Central Pontides
- Eastern Pontides
Istanbul Zone
Strandja Massif
Anatolide-Taurides
Tavsanli Zone
Menderes Massif
Alanya Massif
Bitlis
Massif
Thrace Basin
Neotectonics
and Geomorphology
HIGH AND ULTRAHIGH
PRESSURE METAMORPHIC ROCKS
Ultra-high pressure
rocks in China
Blueschists in the
Tavşanlı Zone in northwest Turkey
HP/LT rocks from
other parts of Turkey
Triassic blueschists and
eclogites related
The
Alanya Massif, Taurides
Precambrian kyanite-eclogites,
the Bitlis Massif, southeast Anatolia
Early Cretaceous blueschists
and eclogites, Central Pontides
Rhodopian
eclogites, northwest Turkey
Enigmatic
blueschists from Thrace
None HP/LT
metamorphic rocks from Turkey
Mineralogy
GENERAL
TECTONICS OF TURKEY AND THE REGION
A
generalized account of the Turkish geology (1), Definition of the Istanbul Zone
as a distinct tectonic unit (2); unmetamorphosed Tauride sequence northwest of
the Menderes Massif: the Bornova Flysch Zone (3); a general synthesis on the
post-Permian tectonic evolution of Turkey with special emphasis on the Pontides
(4).
1. Okay, A.I., 2008; Geology of
Turkey: A synopsis. Anschnitt, 21, 19-42.
2. Okay, A.I., 1989, Tectonic units and sutures in the
Pontides, northern Turkey. In: Tectonic Evolution of the Tethyan Region (ed.
A.M.C. Şengör), NATO Advanced ASI Series, Kluwer Academic Publications,
Dordrecht, 109-116.
3. Okay, A.I., Satır, M., Maluski, H.,
Siyako, M., Monie, P., Metzger, R. & Akyüz S., 1996, Paleo- and Neo-Tethyan events in northwest
Turkey: geological and geochronological constraints. in Tectonics of Asia (ed. A. Yin & M. Harrison), Cambridge
University Press, 420-441.
4. Okay, A.I. & Tüysüz, O.,
1999, Tethyan sutures of northern Turkey.
In "The Mediterranean Basins: Tertiary extension within the Alpine
orogen" (eds. B. Durand, L. Jolivet, F. Horváth
and M. Séranne), Geological Society, London, Special
Publication 156, 475-515.
5. Okay A.I., Tansel, İ. & Tüysüz, O.,
2001, Obduction, subduction and collision as reflected in
the Upper Cretaceous-Lower Eocene sedimentary record of western Turkey. Geological Magazine, 138, 117-142.
6. Okay, A.I., Satır, M. & Siebel, W., 2006, Pre-Alpide orogenic events in the Eastern
Mediterranean region. In: Gee, D.G.
& Stephenson, R.A. (eds.), European
Lithosphere Dynamics. Geological
Society, London, Memoirs 32, 389-405.
7. Stephenson, R., Mart, Y., Okay, A.,
Robertson, A., Saintot, A., Stovba,
S., Khriachtchevskaia, O., 2004, TRANSMED transect
VIII: East European Craton, Crimea, Black Sea, Anatolia, Cyprus, levant Sea,
Sinai, Red Sea. In "The TRANSMED
Atlas - The Mediterranean Region from crust to mantle" (eds. W. Cavazza, F.M. Roure, W. Spakman, G.M. Stampfli, P.A.
Ziegler). Book with CD-ROM, 141 pp., Springer, Heidelberg, Germany.
8.
Okay, A.I. & Nikishin,
A.M., 2015, Tectonic evolution of the southern margin of Laurasia in the Black
Sea region. International Geology Review, 57, 1051-1076.
9.
Okay, A.I. & Topuz, G.,
2017, Variscan orogeny in the Black Sea region. International Journal of Earth
Sciences, 106, 569-592.
Paleotethyan evolution of the eastern
Mediterranean
1. Okay, A.I., 2008; Geology of
Turkey: A synopsis. Anschnitt, 21, 19-42.
2. Okay, A.I. & Tüysüz, O., 1999, Tethyan sutures of northern
Turkey. In "The Mediterranean
Basins: Tertiary extension within the Alpine orogen" (eds. B. Durand, L.
Jolivet, F. Horváth and M. Séranne),
Geological Society, London, Special Publication 156, 475-515.
3. Okay, A.I., Satır,
M. & Siebel, W., 2006, Pre-Alpide
orogenic events in the Eastern Mediterranean region. European Lithosphere Dynamics. Memoir of the Geological Society London (in
press).
4. Okay, A.I. & Göncüoğlu, M.C., 2004, Karakaya
Complex: a review of data and concepts. Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 13,
77-95.
5. Okay, A.I., 2000, Was the Late Triassic orogeny in Turkey
caused by the collision of an oceanic
plateau ? In "Tectonics and
Magmatism in Turkey and Surrounding Area" (eds. E. Bozkurt, J.A. Winchester
and J.A.D. Piper), Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 173, 25-41.
6. Okay, A.I., Siyako, M. & Bürkan, K.A., 1991, Geology and tectonic evolution of the Biga Peninsula.
Special Issue on Tectonics, Bulletin of the Technical University of
Istanbul, 44, 191-255.
7. Okay, A.I. & Mostler,
H., 1994, Carboniferous and Permian radiolarite blocks from the Karakaya Complex
in northwest Turkey. Turkish Journal of
Earth Sciences, 3, 23-28.
8. Okay, A.I., Satır, M., Maluski, H., Siyako, M., Monie,
P., Metzger, R. & Akyüz S., 1996, Paleo- and Neo-Tethyan
events in northwest Turkey: geological and geochronological constraints. in Tectonics of Asia (ed. A. Yin &
M. Harrison), Cambridge University Press, 420-441.
9. Leven, E.Ja. & Okay, A.I.,
1996, Foraminifera from the exotic Permo-Carboniferous limestone blocks in the
Karakaya Complex, northwest Turkey. Rivista Italiana Paleontologia e Stratigrafia,
102, 139-174.
10. Okay, A.I. & Monié, P.,
1997, Early Mesozoic subduction in the Eastern Mediterranean: Evidence from
Triassic eclogite in northwest Turkey.
Geology, 25, 595-598.
11. Okay, A.I., Monod,
O. & Monié, P., 2002, Triassic blueschists and
eclogites from northwest Turkey: vestiges of the Paleo-Tethyan subduction. Lithos, 64, 155-178.
12. Okay, A.I., Satır, M. & Siebel, W., 2006, Pre-Alpide orogenic events in the Eastern
Mediterranean region. In: Gee, D.G.
& Stephenson, R.A. (eds.), European
Lithosphere Dynamics. Geological
Society, London, Memoirs 32, 389-405.
13. Okay, A.I., Noble, P.J. & Tekin, U.K.,.2011, Devonian radiolarian ribbon cherts from the Karakaya
Complex, northwest Turkey: implications for the Paleo-Tethyan evolution. Comptes
Rendus Palevol, 10, 1-10.
14.
Topuz, T., Okay, A.I.,
Schwarz, W.H., Sunal, G., Altherr,
R., Kylander-Clark, A.R.C., 2018, A middle Permian
ophiolite fragment in Late Triassic greenschist- to blueschist-facies rocks in
NW Turkey: An earlier pulse of suprasubduction-zone ophiolite formation in the Tethyan belt. Lithos, 300301, 121135.
Neotethyan evolution of
the eastern Mediterranean
1. Okay, A.I., 2008; Geology of
Turkey: A synopsis. Anschnitt, 21, 19-42.
2. Okay, A.I. & Tüysüz, O., 1999, Tethyan sutures of
northern Turkey. In "The
Mediterranean Basins: Tertiary extension within the Alpine orogen" (eds.
B. Durand, L. Jolivet, F. Horváth and M. Séranne), Geological Society, London, Special Publication
156, 475-515.
3. Okay A.I., Tansel,
İ. & Tüysüz, O., 2001, Obduction,
subduction and collision as reflected in the Upper Cretaceous-Lower Eocene
sedimentary record of western Turkey.
Geological Magazine, 138, 117-142.
4. Okay, A. & Siyako, M., 1993, The revised location of
the İzmir-Ankara Suture in the region between Balıkesir
and İzmir (in Turkish). In: Ozan Sungurlu Symposium
Proceedings, Tectonics and Hydrocarbon Potential of Anatolia and Surrounding
Regions (ed. S. Turgut) , Ankara, 333-355.
5. Okay, A.I. & Tansel, İ., 1994, New data on the upper age of the
Intra-Pontide ocean from north of Şarköy (Thrace).
Bulletin of the Mineral Research and Exploration, 114, 23-26.
6. Okay, A.I., Satır, M., Maluski, H.,
Siyako, M., Monie, P., Metzger, R. & Akyüz S., 1996, Paleo- and Neo-Tethyan events in northwest
Turkey: geological and geochronological constraints. in Tectonics of Asia (ed. A. Yin & M. Harrison), Cambridge
University Press, 420-441.
7. Akyüz, S. & Okay,
A.I., 1996, A section across a Tethyan suture in northwest Turkey. International Geological Review, 38, 405-418.
PONTIDES
Most
of my regional geological studies have been in the Pontides the 1500 km long
east-west trending mountain belt south of the Black Sea. Pontides have been divided into three
terranes: the Istanbul, Sakarya and Strandja.
The Sakarya terrane includes the Central and Eastern Pontides, which are
more of geographic rather than tectonic
terms. Three general papers on the
Pontides are:
Okay, A.I., 2008; Geology of
Turkey: A synopsis. Anschnitt, 21, 19-42.
Okay, A.I. & Tüysüz, O.,
1999, Tethyan sutures of northern Turkey.
In "The Mediterranean Basins: Tertiary extension within the Alpine
orogen" (eds. B. Durand, L. Jolivet, F. Horváth
and M. Séranne), Geological Society, London, Special
Publication 156, 475-515.
Okay, A.I. & Nikishin,
A.M., 2015, Tectonic evolution of the southern margin of Laurasia in the Black
Sea region. International Geology Review, 57, 1051-1076.
Sakarya Zone western part
The Sakarya Zone, especially the western part, is
characterized by voluminous Paleo-Tethyan (Permo-Triassic) subduction-accretion
complexes (Karakaya Complex). For a
general review of the Karakaya Complex including a diifferent ideas for its origin
see (1). The Lower Karakaya Complex
contains latest Triassic eclogites and blueschists (2 and 3) and Permian
ophiolite fragments (13 and 17); metamorphism is mostly Late Triassic but in
places extends into the Early-Middle Jurassic (17). The Upper Karakaya Complex is characterized
by numerous Permo-Carboniferous neritic limestone blocks (4, 5), rare blocks of
Paleozoic radiolarian chert (6 and 10), in situ uppermost Triassic limestone
(7), all with a very low to low grade of metamorphism (9). The Paleozoic crystalline basement of the
Sakarya Zone (16), its Jurassic-Cretaceous (12 and 15) and Eocene (18)
sedimentary cover. Most of the Mesozoic
geology of the Ankara region is represented by huge, crustal-scale
olistostromes of Late Cretaceous (Coniacian) age (15).
Karakaya
Complex
1. Okay, A.I. &
Göncüoğlu,M.C., 2004, Karakaya Complex: a review of data and concepts.
Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 13, 77-95.
2. Okay, A.I. & Monié,
P., 1997, Early Mesozoic subduction in the Eastern Mediterranean: Evidence from
Triassic eclogite in northwest Turkey.
Geology, 25, 595-598.
3. Okay, A.I., Monod, O. & Monié, P., 2002, Triassic blueschists and eclogites from
northwest Turkey: vestiges of the Paleo-Tethyan subduction. Lithos, 64, 155-178.
4. Leven, E.Ja.
& Okay, A.I., 1996, Foraminifera from the exotic Permo-Carboniferous
limestone blocks in the Karakaya Complex, northwest Turkey. Rivista Italiana Paleontologia e Stratigrafia, 102, 139-174.
5. Okay, A.I., Siyako, M. & Bürkan,
K.A., 1991, Geology and tectonic evolution of the Biga
Peninsula. Special Issue on Tectonics,
Bulletin of the Technical University of Istanbul, 44, 191-255.
6. Okay, A.I. & Mostler, H.,
1994, Carboniferous and Permian radiolarite blocks from the Karakaya Complex in
northwest Turkey. Turkish Journal of
Earth Sciences, 3, 23-28.
7. Okay, A.I. &
Altıner, D., 2004, Uppermost Triassic limestone in the Karakaya Complex -
stratigraphic and tectonic significance. Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 13,
187-199.
9. Federici,
I., Cavazza, W., Okay, A.I., Beyssac, O., Zattin, M., Corrado, S. &
Dellisanti, F. 2010. Thermochronologic evolution
of the Permo-Triassic Karakaya subduction-accretion complex from the Biga Peninsula to the Tokat
Massif (Anatolia). Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 19, 409-429.
10.
Okay, A.I., Noble, P.J. & Tekin, U.K.,.2011, Devonian radiolarian ribbon cherts from the Karakaya
Complex, northwest Turkey: implications for the Paleo-Tethyan evolution.
Comptes Rendus Palevol, 10, 1-10.
13.
Topuz, T., Okay, A.I.,
Schwarz, W.H., Sunal, G., Altherr,
R., Kylander-Clark, A.R.C., 2018, A middle Permian
ophiolite fragment in Late Triassic greenschist- to blueschist-facies rocks in
NW Turkey: An earlier pulse of suprasubduction-zone ophiolite formation in the Tethyan belt. Lithos, 300301, 121135
Stratigraphy
8. Yıkılmaz, M.B.,
Okay, A.I. & Tansel, İ., 2002, A pelagic Palaeocene sequence in the Biga
Peninsula, northwest Turkey. Bulletin of
the Mineral Research and Exploration, 123/124, 21-26.
12. Okay, A.I., Altıner,
D., 2016, Carbonate sedimentation in an active margin: Cretaceous history of
the Haymana region, Pontides. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 105,
20132030.
Atasoy, S.G., Altiner, D., Okay, A.I.,
2018, Reconstruction of a Late JurassiceEarly
Cretaceous carbonate platform margin with composite biostratigraphy and
microfacies analysis (western Sakarya Zone, Turkey): Paleogeographic and
tectonic implications. Cretaceous
Research, 92, 66-93.
Okay, A. I., Altıner, D.
& Kylander‐Clark, A. R. C. (2019). Major
Late Cretaceous mass flows in central Turkey recording the disruption of the
Mesozoic continental margin. Tectonics, 38, 960-989.
Özcan, E., Yücel,
A.O., Catanzariti, R., Kayğılı,
S., Okay, A.I., Simmons, M.D., Pignatti, J., Abbasi, I.A. & Erbil, Ü., 2021, Multiple Orbitoides dOrbigny lineages in
the Maastrichtian? Data from the Central
Sakarya Basin (Turkey) and Arabian Platform successions (Southeastern
Turkey and Oman). Swiss Journal of Palaeontology, 140:8.
Özcan, E., Hakyemez,
A., Çiner, A., Okay, A.I., Soussi,
M., Boukhalfa, K. & Yücel,
A.O., 2020, A reinterpretation of the age and depositional environment of the Eocene
Çayraz Formation (Haymana
Basin, Central Turkey) in the light of new planktonic foraminiferal data.
Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 183, article 104304.
Yücel, A.O., Özcan,
E., Catanzariti, R., Hakyemez,
A., Okay, A.I., Çiner, A. & Akın, A., 2023,
Calcareous nannofossils, planktonic foraminifera and revised stratigraphy of
the Eocene Çayraz Formation; the final stage of
marine sedimentation in Central Turkey. Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 32,
1-26.
Variscan
and older basement
16.
Topuz, G., Candan,
O., Okay, A.I., von Quadt, A., Othman, M., Zack, T.
& Wang, J., 2020, Silurian anorogenic basic and acidic magmatism in
northwest Turkey: Implications for the opening of the Paleo-Tethys. Lithos, 356-357, article 105302.
Sakarya Zone central part - Central Pontides
A general account of the geology of the Central
Pontides (1). In the south an immense
accretionary complex with Jurassic, Lower and Upper Cretaceous (Neo-Tethyan)
accretionary complexes (2, 7, 8 and 9). In
the north a preserved segment of a Triassic forearc sequence (6); an
interesting case of HT metamorphism at deeper levels of a Jurassic arc (5) and
a huge Lower Cretaceous submarine turbidite fan, which extended from Baltica (Ukranian shield) south
to the Tethyan trench (4, 10 and 11).
1.
Okay, A.I., Altıner, D., Sunal, G., Tüysüz, O., Aygül, M.,
Akdoğan, R., Altıner, S., Simmons, M.,
2018, Geological Evolution of the Central Pontides. In: Simmons, M.D., Tari, G.C. & Okay,
A.I. (eds), Petroleum Geology of the Black Sea, Geological Society, London,
Special Publications, 464, 3367.
2.
Okay, A.I., Tüysüz, O., Satır, M., Özkan-Altıner,
S., Altıner, D., Sherlock, S., & Eren, R.H.,
2006, Cretaceous and Triassic subduction-accretion, HP/LT metamorphism and
continental growth in the Central Pontides, Turkey. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 118,
1247-1269.
3.
Federici, I., Cavazza, W., Okay, A.I., Beyssac,
O., Zattin, M., Corrado,
S. & Dellisanti, F. 2010. Thermochronologic
evolution of the Permo-Triassic Karakaya subduction-accretion complex from the Biga Peninsula to the Tokat
Massif (Anatolia). Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 19, 409-429.
4.
Okay, A.I., Sunal, G., Sherlock, S., Altıner, D., Tüysüz, O., Kylander-Clark, A.R.C. & Aygül,
M., 2013, Early Cretaceous sedimentation and orogeny on the active margin of
Eurasia: southern Central Pontides, Turkey. Tectonics, 32, 1247-1271.
5.
Okay, A.I., Sunal, G., Tüysüz, O., Sherlock, S., Keskin,M.
& Kylander-Clark, A.R.C., 2014, Low-pressure -
high-temperature metamorphism during extension in a Jurassic magmatic arc,
Central Pontides, Turkey. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 32, 49-69.
6.
Okay, A.I., Altıner, D.
& Kılıç, A.M., 2015, Triassic
limestone, turbidites and serpentinitethe Cimmeride orogeny in the Central
Pontides. Geological Magazine, 152,
460-479.
7.
Aygül, M., Okay, A.I., Oberhaensli, R. & Ziemann,
M.A., 2015, Thermal structure of low-grade accreted Lower Cretaceous distal
turbidites, the Central Pontides, Turkey: insights for tectonic thickening of
an accretionary wedge. Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 24, 461-474.
8.
Aygül, M., Okay, A.I., Oberhänsli, R., Schmidt, A., Sudo,
M., 2015, Late Cretaceous infant intra-oceanic arc volcanism, the Central
Pontides, Turkey: Petrogenetic and tectonic implications. Journal of Asian
Earth Sciences, 111, 312-327.
9.
Aygül, M., Okay, A.I., Oberhänsli, R., Sudo, M., 2016,
Pre-collisional accretionary growth of the southern Laurasian margin, Central
Pontides, Turkey. Tectonophysics, 671, 218234.
10. Akdoğan, R.. Okay, A.I., Sunal, G., Tari, G., Meinhold, G. &
Kylander-Clark, A.R.C., 2017, Provenance of a large Lower Cretaceous turbidite
submarine fan on the active Laurasian margin. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences
134, 309329.
11. Akdoğan, R., Okay, A. I. & Dunkl, I. (2019). Striking variation in
the provenance of the Lower and Upper Cretaceous turbidites in the central
Pontides (northern Turkey) related to the opening of the Black Sea. Tectonics,
38, 1050-1069.
Sakarya Zone eastern part - Eastern Pontides
One of the best preserved island arcs, a general
review of its geology (1, 6), data on its heterogeneous pre-Liassic basement
(3-5 and 7). Detrital zircons in Jurassic volcaniclastic rocks revealing
Triassic and Jurassic arc magmatism (8).
1. Okay, A.I. & Şahintürk,
Ö., 1997 Geology of the Eastern Pontides. In "Regional and Petroleum
Geology of the Black Sea and Surrounding Region" (ed. A.G. Robinson),
American Association of Petroleum Geologists (AAPG) Memoir No. 68, 291-311.
2. Okay, A.I., 1984, The geology
of the Ağvanis metamorphic rocks and neighbouring formations.
Bulletin of the Mineral Research and Exploration Institute of Turkey,
99/100, 16-36.
3. Okay, A.I.,
1996, Granulite facies gneisses from the Pulur region, Eastern Pontides. Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 5, 55-61.
4. Okay, A.I. & Leven, E.Ja., 1996, Stratigraphy and paleontology of the Upper
Paleozoic sequence in the Pulur (Bayburt)
region, Eastern Pontides. Turkish
Journal of Earth Sciences, 5, 145-155.
5. Okay, A.I., Şahintürk,
Ö. & Yakar, H., 1997, Stratigraphy and tectonics
of the Pulur (Bayburt)
region in the Eastern Pontides. Bulletin of the Mineral Research and
Exploration Institute of Turkey, 119,
1-24.
6. Konak, N., Okay, A.I.,
Hakyemez, Y., 2009, Tectonics and Stratigraphy of the Eastern Pontides. Field
trip guide book, Maden Tetkik ve Arama Genel Müdürlüğü ve TMMOB Jeoloji
Mühendisleri Odası, Ankara, ISBN 978-9944-897-83-9, 120 pp.
7. Topuz, G., Okay, A.I., Altherr, R., Schwarz, W.H., Sunal, G.,
Altınkaynak, L., 2014, Triassic warm subduction in the northeast Turkey:
Evidence from the Ağvanis metamorphic rocks. Island Arc, 23, 181205.
8. Akdoğan, R.. Okay,
A.I., Dunkl, I., 2018, Triassic-Jurassic Arc Magmatism in the Pontides as
Revealed by the U-Pb Detrital Zircon Ages in the Jurassic Sandstones,
Northeastern Turkey. Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 27, 89-109.
9. Özcan, E., van Gorsel, J.T.,
Sarı, B., Yücel, A.O., Erbay, S. & Okay, A.I., 2019, Primitive
Helicorbitoides (Foraminifera) and associated larger benthic foraminifera from
the Campanian Tonya Formation, Trabzon, eastern Pontides, NE Turkey. Cretaceous
Research, 101, 30-42.
10. Topuz, G.,
Altherr, R., Candan, O., Wang,
J., Okay, A.I., Wu, F-Y., Ergen, A., Zack, T., Siebel, W., Shang, C.K., Schwarz, W.H., Meyer, H-P., Satır, M., 2023, Carboniferous
mafic-ultramafic intrusions
in the Eastern Pontides
(Pulur Complex): Implications
for the source
of coeval voluminous granites. Lithos, 436437,
106946.
Istanbul Zone
An exotic continental terane representing a long standing
Paleozoic passive continental margin sequence.
A tectonic model for its Late Cretaceous evolution (1); data on its
Paleozoic (2 & 5) and Late Cretaceous (6) stratigraphy and its Paleozoic
location based on detrital zircon-rutile geochronology (3 and 7);
geochronological data on its Pre-Cambrian and Ordovician basement in the
Armutlu Peninsula, southeast of Istanbul (4).
1. Okay, A.I., Şengör, A.M.C. &
Görür, N., 1994, Kinematic history of the opening of the Black Sea and its
effect on the surrounding regions.
Geology, 22, 267-270 .
2. Görür, N., Monod, O., Okay, A.I.,
Şengör, A.M.C., Tüysüz, O., Yiğitbaş, E., Sakınç,
M. & Akkök, R., 1997, Palaeogeographic and
tectonic position of the Carboniferous rocks of the western Pontides (Turkey)
in the frame of the Variscan belt.
Bulletin de la Société Géologique
de France, 168, 197-205.
3. Okay, N., Zack, T., Okay, A.I.
& Barth, M. 2011, Sinistral
transport along the Trans-European Suture Zone: detrital zircon-rutile
geochronology and sandstone petrography from the Carboniferous flysch of the
Pontides. Geological Magazine, 148, 380-403.
4. Özgörüş, Z., & Okay, A.I., 2005,
Orientation of the Cretaceous dykes in the Istanbul region: an approach to the
Cretaceous stress distribution. Bulletin of the Mineral Research and Exploration,
130, 17-27.
4. Okay, A.I., Bozkurt, E., Satır, M., Yiğitbaş, E., Crowley, Q.G. &
Shang, C.K., 2008, Defining the southern margin of Avalonia in the Pontides:
geochronological data from the Late Proterozoic and Ordovician granitoids from
NW Turkey. Tectonophysics, 461, 252-264.
5. Okay, A.I., Atakul-Özdemir, A. & Okay, N., 2020, A pelagic Upper
Devonian sequence in Sarıyer, Istanbul. Turkish
Journal of Earth Sciences, 29, 785-797.
6. Erdem, M.E., Özcan,
E., Yücel, A.O., Okay, A.I., Erbay, S., Kaygılı, S. & Yılmaz, İ., 2021,
Late Campanian larger benthic foraminifera from the Zekeriyaköy
Formation (İstanbul, NW Turkey): taxonomy, stratigraphy and palaeogeography. Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 30:
1-21.
7. Akdoğan,
R., Hu, X., Okay, A.I., Topuz, G., & Xue, W.,
2021, Provenance of the Paleozoic to Mesozoic siliciclastic rocks of the Istanbul Zone constrains the
timing of the Rheic Ocean closure in the Eastern
Mediterranean region. Tectonics, 40, e2021TC006824.
8. Akdoğan, R., Dunkl,
I., Okay, A.I., Hu, X. & Topuz, G., 2022, Records of latest Triassic,
mid-Cretaceous and Cenozoic uplift/exhumation phases in the Istanbul zone
revealed by apatite fission-track and (U-Th)/He thermochronology. International
Geology Review, 64, 297310.
Strandja
Massif
Late Hercynian and Late Jurassic-Early
Cretaceous deformation and metamorphism in the Balkans.
Okay, A.I., Satır, M., Tüysüz, O., Akyüz,
S. & Chen, F., 2001, The tectonics of the Strandja
Massif: Variscan and mid-Mesozoic deformation and metamorphism in the northern
Aegean. International Journal of Earth Sciences (Geologische Rundschau), 90,
217-233.
Cattò, S., Cavazza,
W., Zattin, M., Okay, A.I., 2018, No significant
Alpine-age tectonic overprint of the Cimmerian Strandja Massif (SE Bulgaria and
NW Turkey). International Geology Review, 60, 513529.
Black Sea
An
oceanic back-arc basin of Late Cretaceous age with a thick sedimentary cover.
Okay, A.I., Şengör,
A.M.C. & Görür, N., 1994, Kinematic history of the opening of the Black Sea
and its effect on the surrounding regions.
Geology, 22, 267-270.
Nikishin, A.M., Okay, A.I.,
Tüysüz, O., Demirer, A., Amelin,
N. & Petrov, E., 2015, The Black Sea basins structure and history: New
model based on new deep penetration regional seismic data. Part 1: Basins
structure and fill. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 59, 638-655.
Nikishin, A.M., Okay, A.,
Tüysüz, O., Demirer, A., Wannier,
M., Amelin, N. & Petrov, E., 2015, The Black Sea
basins structure and history: New model based on new deep penetration regional
seismic data. Part 2: Tectonic history and paleogeography. Marine and Petroleum
Geology, 59, 656-670.
Simmons, M.D., Tari, G.C.
& Okay, A.I., 2018. Petroleum Geology of the Black Sea: introduction. In: Simmons, M.D., Tari, G.C. & Okay,
A.I. (eds), Petroleum Geology of the Black Sea, Geological Society, London,
Special Publications, 464, 1-18.
SUTURES,
OPHIOLITE AND OPHIOLITIC MELANGES
1.
Okay, A. I., Sunal, G., Sherlock, S., Kylander-Clark,
A. R. C., & Özcan, E. (2020). İzmir-Ankara
suture as a Triassic to Cretaceous plate boundaryData from central Anatolia.
Tectonics, 38. e2019TC005849.
2.
Okay, A.I., Altıner, D., Danelian, T., Topuz, G., Özcan,
E. & Kylander‐Clark, A.R.C., 2022,
Subduction-accretion complex with supra-subduction-zone ophiolite slices:
Ankara Mélange, central Anatolia. Geological Magazine 159, 16991726.
3.
Akbayram, K., Okay. A.I. & Satır, M., 2013. Early Cretaceous closure of the
Intra-Pontide Ocean in western Pontides (northwestern
Turkey). Journal of Geodynamics, 65, 38-55.
4.
Okay, A.I., Altıner, D., Danelian, T., Topuz, G., Özcan,
E. & Kylander‐Clark, A.R.C., 2022,
Subduction-accretion complex with supra-subduction-zone ophiolite
slices: Ankara Mélange, central Anatolia. Geological Magazine 159, 16991726.
ANATOLIDE-TAURIDES
The
Anatolide-Taurides comprises the tectonic zones south of the Izmir-Ankara
suture. In general the metamorphic units
in the north (Menderes Massif, Tavsanli Zone and the Kirsehir Massif) are
called Anatolides, and the sedimentary nappe units in
the south the Taurides, although there are several exceptions.
Tavsanli
Zone
A
250-km-long, Late Cretaceous high pressure metamorphic belt on the northern
margin of the Anatolide-Tauride Block representing the subducted northern margin
of the continental crust. A general
review of its tectonic setting (1), constraints and ideas on its exhumation
(2), Eocene plutonism (3 and 4).
1. Okay, A.I., 1984,
Distribution and characteristics of the northwest Turkish blueschists. In: The Geological Evolution of the Eastern
Mediterranean (ed. J.E. Dixon & A.H.F. Robertson), Geological Society Special Publication No.
17, 455-466.
Okay, A.I., 1985, Metamorphic
belts in northwest Anatolia (in Turkish). In: Ketin Symposium Book, Publication
of the Geological Society of Turkey, Ankara, 83-92.
2. Okay, A.I., Harris, N.B.W. &
Kelley, S.P., 1998, Exhumation of blueschists along a Tethyan suture in
northwest Turkey. Tectonophysics, 285,
275-299.
3. Harris, N.B.W., Kelley, S. &
Okay, A.I., 1994, Post-collision magmatism and tectonics in northwest
Anatolia. Contributions to Mineralogy
and Petrology, 117, 241-252.
4. Okay, A.I. & Satır,
M., 2006, Geochronology of Eocene plutonism and metamorphism in northwest
Turkey: evidence for a possible magmatic arc.
Geodinamica Acta,
19, 251-266.
5. Okay, A.I. & Whitney,
D.L., 2010, Blueschists, ophiolites and suture zones in northwest Turkey. Field trip guidebook.
6. Plunder, A., Agard, P.,
Chopin, C. & Okay, A.I., 2013, Geodynamics of the Tavşanlı zone,
western Turkey: Insights into subduction/obduction processes. Tectonophysics,
608, 884-903.
7. Plunder, A., Agard, P.,
Chopin, C., Pourteau, A. & Okay,
A.I., 2015, Accretion, underplating and exhumation along a subduction
interface: From subduction initiation to continental subduction
(Tavşanlı zone,W. Turkey). Lithos, 226, 233-254.
8. Plunder, A., Agard, P., Chopin, C., Soret, M.,
Okay, A.I., Whitechurch, H., 2016, Metamorphic sole
formation, emplacement and blueschist overprint: early obduction dynamics
witnessed by Western Turkey ophiolites. Terra Nova, 28, 329339.
9. Pagé,
L.,Hattori, K., de Hoog,
J.C.M. & Okay, A.I., 2016, Halogen (F, Cl, Br, I) behaviour in subducting slabs:
A study of lawsonite blueschists in western Turkey. Earth and Planetary Science
Letters, 442, 133142.
Menderes
Massif
A
large, well-studied metamorphic complex in the Aegean. Eocene Barrovian type metamorphism. Unorthodox ideas on its structure (1 and 2).
relationship with the overlying Lycian nappes (3). Support for the recumbent
fold structure of the Menderes Massif (5).
Carboniferous metagranites on the northern margin of the Menderes Massif
(4).
1. Okay, A.I., 2001, Stratigraphic and
metamorphic inversions in the central Menderes Massif: a new structural
model. International Journal of Earth
Sciences (Geologische Rundschau),
89, 709-727.
2. Okay, A.I., 2002, Reply:
Stratigraphic and metamorphic inversions in the central Menderes Massif: a new
structural model. International Journal
of Earth Sciences (Geologische Rundschau),
91, 173-178.
3. Okay, A.I., 1989, Geology of the Menderes Massif and the
Lycian nappes south of Denizli,
western Taurides. Bulletin of the
Mineral Research and Exploration of Turkey, 109, 37-51.
4. Candan, O., Akal, C., Koralay, O.E., Okay, A.I., Oberhänsli,
R., Prelević, D., Mertz-Kraus, R., 2016,
Carboniferous granites on the northern margin of Gondwana, Anatolide-Tauride
Block, Turkey - evidence for southward subduction of Paleotethys.
Tectonophysics, 683, 349366.
5. Gülmez, F., Damcı,
E., Ülgen, U.B. & Okay, A.I., 2019, Deep
structure of Central Menderes Massif: data from deep geothermal wells. Turkish
Journal of Earth Sciences 28, 531-543.
Bornova
Flysch Zone
A
60-km-wide tectonic belt northwest of the Menderes Massif consisting of Mesozoic
limestone and ophiolite blocks in a chaotically deformed flysch matrix of
latest Cretaceous age. First definition
of the Bornova Flysch Zone (1) and a condensed limestone section extending from
Late Triassic (Norian) to Late Cretaceous (Turonian) (2), a general account of
the BFZ with many new stratigraphic sections and a revised model (3), source of
the Bornova flysch (4).
1. Okay, A. &
Siyako, M., 1993, The revised location of the İzmir-Ankara Suture in the
region between Balıkesir and İzmir (in
Turkish). In: Ozan
Sungurlu Symposium Proceedings, Tectonics and
Hydrocarbon Potential of Anatolia and Surrounding Regions (ed. S. Turgut) ,
Ankara, 333-355.
2. Okay, A.I. &
Altıner, D., 2007, A condensed
Mesozoic section in the Bornova Flysch Zone: A
fragment of the Anatolide-Tauride carbonate platform. Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 16, 257-279.
3. Okay, A.I.,
İşintek, İ., Altıner, D., Özkan-Altıner, S., Okay, N.,
2012, An olistostrome- mélange belt formed along a major suture: Bornova Flysch
Zone, western Turkey. Tectonophysics, 568-569,
282-295.
4. Okay, A.I. & Kylander-Clark, A.R.C., 2023, No sediment transport across the Tethys ocean
during the latest Cretaceous: detrital zircon record from the
Pontides and the
Anatolide-Tauride Block. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 112,
9991022.
Alanya Massif
A
composite metamorphic nappe in the uppermost structural level in the Taurides
on the Mediterranean coast. It consists
of three thin but continuous nappes; the middle one is metamorphosed in the
eclogite facies.
Okay, A.I. & Özgül, N., 1984, HP/LT metamorphism
and the structure of the Alanya Massif, Southern
Turkey: an allochthonous composite tectonic sheet. In: The Geological Evolution of the Eastern
Mediterranean (ed. J.E. Dixon &
A.H.F. Robertson), Geological Society Special Publication No. 17, 429-439.
Okay. A.I., 1989, An exotic
eclogite/blueschist slice in a Barrovian-style metamorphic
terrain, Alanya Nappes, southern Turkey. Journal of
Petrology, 30, 107-132.
Çetinkaplan, M., Pourteau, A.,
Candan, O., Koralay, O.E., Oberhänsli,
R., Okay, A.I., Chen, F., Kozlu, H. & Şengün, F., 2016, P-T-t evolution of
eclogite/blueschist facies metamorphism in Alanya
Massif: time and space relations with HP event in Bitlis Massif, Turkey.
International Journal of Earth Sciences, 105, 247281.
Bitlis
Massif and Southeast Anatolia
Tectonically
imbricated metamorphic slices in southeast Anatolia north of the Assyrian
suture. The Bitlis Massif includes both
basement slices with kyanite-eclogites and upper crustal slices with
greenschist facies metamorphism. Recent
work has shown an Alpine (Late Cretaceous) high pressure - low temperature
metamorphism in the Bitlis Massif. A relative recent discovery is the very high
temperature granulite facies metaophiolites from
below the Bitlis Massif.
Okay, A.I., Arman, M.B. &
Göncüoğlu, M.C., 1985, Petrology and phase relations of the
kyanite-eclogites from eastern Turkey.
Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 91, 196-204.
Oberhänsli, R., Candan, O.,
Bousquet, R, Rimmele, G., Okay, A. I., Goff, B.J., 2010, Alpine HP evolution of
the eastern Bitlis complex, SE Turkey.
In: Sedimentary basin tectonics from the Black Sea and
Caucasus to the Arabian Platform (eds. M. Sosson,
N. Kaymakçı, R. Stephenson, V. Starostenko, F. Bergerat, Geological
Society, London, Special
Publication, 340, 461-483.
Oberhänsli, R., Bousquet, R.,
Candan, O. & Okay, A.I., 2012, Dating subduction events in East Anatolia,
Turkey. Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 21, 1-17.
Karaoğlan, F., Parlak,
O., Robertson, A., Thöni, M., Klötzli, U., Koller, F. & Okay, A.I., 2013,
Evidence of Eocene high-temperature metamorphism of ophiolitic rocks and
granitoid intrusion related to Neotethyan subduction processes
(Doğanşehir area, SE Anatolia). Geological Society, London, Special
Publication, 372, 249-272.
Thrace
Basin
A
large hydro-carbon bearing clastic basin of Eocene-Oligocene age northwest of Istanbul.
Stratigraphy and geological development of the basin (1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9, 12, 13,
16 and 17), olistostromal Eocene facies in the southern Thrace basin (4, 7 and
8), tectonic development of the basin (5, 6 and 17), sandstone petrography and
provenance (10). Relationship to the Black Sea basin during the early Tertiary
(13, 14 and 15).
1. Görür, N.
& Okay, A.I., 1996, Fore-arc origin of the Thrace basin, northwest Turkey. Geologische Rundschau 85, 662-668.
2.
Okay, A.I., Siyako, M. & Yurtsever, A., 2007,
Lithostratigraphic units in Thrace. Maden Tetkik ve
Arama Genel Müdürlüğü, Ankara (baskıda).
3. Siyako, M., Bürkan, K.A. & Okay, A.I., 1989, Tertiary geology and
hydrocarbon potential of the Biga and Gelibolu peninsulas (in Turkish). Bulletin of the Turkish Association of
Petroleum Geologists, 1, 183-199.
4. Okay, A.I. & Tansel, İ., 1994, New data on the upper age of the
Intra-Pontide ocean from north of Şarköy
(Thrace). Bulletin of the Mineral
Research and Exploration, 114, 23-26.
5. Okay, A.I., Tüysüz, O.
& Kaya, Ş., 2004, From transpression to
transtension: Changes in morphology and structure around a bend on the North
Anatolian Fault in the Marmara region. Tectonophysics, 391, 259-282.
6. Zattin, M., Okay, A.I.
& Cavazza, W., 2005. Fission-track evidence for late
Oligocene and mid-Miocene activity along the North Anatolian Fault in south-western
Thrace. Terra Nova, 17, 95-101.
7. Okay; A.I., Özcan, E., Cavazza, W., Okay; N. & Less,
G. 2010. Basement types, Lower Eocene series, Upper Eocene olistostromes and the
initiation of the southern Thrace Basin, NW Turkey. Turkish Journal of Earth
Sciences, 19, 1-25.
8. Özcan, E., Less, G., Okay, A.I.,
Báldi-Beke, M., Kollányi, K. & Yilmaz, İ.Ö. 2010. Stratigraphy and larger foraminifera of the
Eocene shallow-marine and olistostromal units of the southern part of the
Thrace Basin, NW Turkey. Turkish
Journal of Earth Sciences, 19, 27-77.
9. Less, G., Özcan, E. &
Okay, A.I., 2011, Stratigraphy and
larger foraminifera of the Middle Eocene to Lower Oligocene shallow-marine
units in the northern and eastern parts of the Thrace Basin, NW Turkey. Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 20,
793-845.
10. DAtri, A., Zuffa, G.G.,
Cavazza, W., Okay, A.I. & Di Vincenzo, G., 2012, Detrital supply from
subduction/accretion complexes to the EoceneOligocene post-collisional
southern Thrace Basin (NW Turkey and NE Greece). Sedimentary Geology, 243-244, 117-129.
11. Okay, A.I. & Özcan, E., 2014, Faulting, basement uplift and carbonate
sedimentation: Çatalca region, west of Istanbul. Field trip guidebook, AAPG International
Conference & Exhibition 2014, Istanbul, Turkey, pre-conference field trip
4, September 13, 2014, Turkish Association of Petroleum Geologists, Ankara, 15
pp.
12. Özcan, E., Okay, A.I., Bürkan, K.A., Yücel, A.O., Özcan, Z., 2018, The Bartonian-Priabonian marine record of
the Biga Peninsula, NW Anatolia (Turkey): larger
benthic foraminifera, revised stratigraphy and implications for the regional
geology. Geologica Acta,
16, 163-187.
13. Okay, A.I., Özcan, E., Hakyemez, A., Siyako,
M., Sunal, G., Kylander-Clark,
A.R.C., 2019, The Thrace Basin and the Black Sea: the Eocene - Oligocene
connection. Geological Magazine, 156, 39-61.
14. Okay, A.I., Simmons, M., Özcan, E., Starkie, S., Bidgood, M. & Kylander-Clark, A.R.C., 2020, Eocene-Oligocene succession
at Kıyıköy (Midye)
on the Black Sea coast in Thrace. Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 29,
139-153.
15. Simmons, M.D., Bidgood, M.D.,
Connell, P.G., Ćorić, S., Okay, A.I., Shaw,
D., Tulan, E., Mayer, J. & Tari, G.C., 2020,
Biostratigraphy and palaeoenvironments of the
Oligocene succession (Ihsaniye Formation) at Karaburun (NW Turkey). Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences,
29, 28-63.
16. Özcan, E., Özcan,
Z., Okay, A.I., Akbayram, K. & Hakyemez, A., 2020, Ypresian-to Lutetian marine record in
NW Turkey: a revised biostratigraphy and chronostratigraphy
and implications for the Eocene paleogeography. Turkish Journal of Earth
Sciences, 29, 1-27.
17. Erbil, Ü., Okay, A.I.
& Hakyemez, A., 2021, Late OligoceneEarly
Miocene shortening in the Thrace Basin, northern Aegean. International Journal
of Earth Sciences, 110, 19211936.
18. Özcan, E., Yücel,
A.O., Mitchell, S., Pignatti, J., Okay, A.I., Gültekin, M.N., Yurtsever, S.
& Erkızan, L.S., 2022, New
records of Caudriella Haman and Huddleston from the
middle and late Eocene of Neo-Tethys: palaeobiogeographic
implications. The Journal of Foraminiferal Research,
52, 2139.
Post-collisional
metamorphic core complexes, neotectonics, magmatism and geomorphology
Uludag Massif
A major Oligocene dextral shear zone in western
Anatolia: Eskişehir Fault and the Uludağ Massif an earlier start
for the escape tectonics Oligocene granites, one is highly sheared.
Okay, A.I.,
Satır, M., Zattin, M., Cavazza, W. & Topuz, G., 2008, An Oligocene
ductile strike-slip shear zone: Uludağ Massif, northwest Turkey
implications for the escape tectonics. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 120, 893911.
Topuz, G. & Okay, A.I.,
2017, Late Eocene - Early Oligocene two-mica granites in NW Turkey (the
Uludağ Massif): Water-fluxed melting products of a mafic metagraywacke.
Lithos, 268271, 334350.
Kazdağ Massif
Oligo-Miocene extension of the lower crust of
western Anatolia: Kazdağ Massif
Okay, A.I. & Satır, M., 2000, Coeval plutonism and metamorphism in
a latest Oligocene metamorphic core complex in northwest Turkey. Geological Magazine, 137, 495-516.
Cavazza, W., Okay, A.I. &
Zattin, M., 2009, Rapid early-middle Miocene exhumation of the Kazdağ
metamorphic core complex (Western Anatolia). International Journal of Earth
Sciences (Geol Rundsch), 98, 19351947.
North Anatolian Fault
Geometry of the North Anatolian Fault and submarine
strike-slip basins in the Marmara Sea (1,2), rearrangment of drainage and
morphology through fault activity (3), evidence for earlier fault activity
along the North Anatolian Fault (5, 6).
1. Okay, A.I., Demirbağ,
E., Kurt, H., Okay, N. & Kuşçu, İ.,
1999, An active, deep marine strike-slip basin along the North Anatolian fault
in Turkey. Tectonics, 18, 129-148.
2. Okay, A. I., Kaşlılar-Özcan,
A., İmren, C., Boztepe-Güney,
A., Demirbağ, E. & Kuşçu,
İ. 2000, Active faults and evolving strike slip basins in the Marmara Sea,
northwest Turkey: a multi-channel seismic reflection study. Tectonophysics, 321, 189-218.
3. Okay, N. & Okay, A.I., 2002, Tectonically induced Quaternary
drainage diversion in northeastern Aegean. Journal of
the Geological Society, London, 159, 393-400.
4. Okay, A.I., Tüysüz, O. & Kaya,
Ş., 2004, From transpression to transtension:
Changes in morphology and structure around a bend on the North Anatolian Fault
in the Marmara region. Tectonophysics, 391, 259-282.
5. Zattin, M.,
Okay, A.I. & Cavazza, W., 2005. Fission-track
evidence for late Oligocene and mid-Miocene activity along the North Anatolian
Fault in south-western Thrace. Terra
Nova, 17, 95-101.
6. Janssen, C., Bohnhoff, M., Vapnik,
Y., Gorgun, E., Bulut, F., Plessen, B., Pohl, D., Aktar, M.,
Okay, A.I., Dresen, G., 2009, Tectonic evolution of
the Ganos segment of the North Anatolian Fault (NW
Turkey). Journal of Structural Geology,
31, 11-28.
7. Zattin, M., Cavazza, W., Okay, A.I., Federici, I.,
Fellin, M.G., Pignalosa, A. & Reiners, P. 2010. A precursor of the North
Anatolian Fault in the Marmara Sea region. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 39, 97108.
8. Akbayram, K., Sorlien,
C. & Okay, A.I., 2016, Evidence for a minimum 52±1 km of total offset along
the northern branch of the North Anatolian Fault in northwest Turkey.
Tectonophysics, 668-669, 35-41.
Bitlis collision zone
Apatite fission track data showing Miocene collision
between Arabia and Eurasia.
Okay, A.I., Zattin, M. &
Cavazza, W., 2010, Apatite fission-track data for Miocene Arabia-Eurasia
collision. Geology, 38, 35-38.
Albino, I., Cavazza, W., Zattin, M., Okay, A.I., Adamia, S. & Sadradze, N., 2014, Far-field tectonic effects of the
Arabia-Eurasia collision and the inception of the North Anatolian Fault system.
Geological Magazine, 151, 372379.
Cavazza, W., Cattò,
S., Zattin, M., Okay,A.I.
& Reiners, P., 2018, Thermochronology of the
Miocene Arabia-Eurasia collision zone of southeastern
Turkey: Geosphere, 14, 117.
Vincent, S. J., Saintot, A., Mosar, J., Okay, A.
I., & Nikishin, A. M., 2018, Comment on Relict basin closure andcrustal shortening budgets during continental collision:
An example from Caucasus sediment provenance by Cowgill et al. (2016).
Tectonics, 37. 2017TC004515.
Post-collisional magmatism
Okay, A.I., Topuz, T., Kylander-Clark, A.R.C., Sherlock, S. & Zattin, M., 2022, Late Paleocene
Middle Eocene magmatic flare-up in western Anatolia. Lithos,
428429, 106816.
Geomorphology
An early fluviatile network in the western Taurides
(1), a major river diversion in Thrace (2) and when and hwy
did Anatolia became a land area (3, 4, 5)?
1. Monod, O., Kuzucuoğlu,
C. & Okay, A.I., 2006, A Miocene paleovalley
network in the Western Taurus (Turkey).
Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 15, 1-23.
2. Okay, N. & Okay, A.I.,
2002, Tectonically induced Quaternary drainage diversion in northeastern
Aegean. Journal of the Geological Society, London, 159, 393-400.
3. Okay, A. I.,Zattin, M., Özcan, E., & Sunal, G. 2020, Uplift of Anatolia. Turkish Journal of
Earth Sciences, 29, 696-713.
4. Okay, A.I., Zattin, M., Özcan, E., & Sunal, G. 2021, Anadolunun yükselmesi. MTA Doğal Kaynaklar ve Ekonomi Bülteni,
31: 1-11.
5. Okay, A.I., 2022, Scientific
Comment on McPhee et al Preparing the ground for plateau growth: Late Neogene
Central Anatolian uplift in the context of orogenic
and geodynamic evolution since the Cretaceous, Tectonophysics
822, 229131.
HIGH
AND ULTRA-HIGH PRESSURE METAMORPHIC ROCKS
Ultra-high
pressure rocks in China
Papers
on the petrology and tectonics of the worlds largest
UHP terrain; the description of the first coesite in garnet and dolomite in
Dabie Shan (1,9), tectonic model for exhumation of the UHP metamorphic rocks
(3,4), degree of reequilibration within the eclogite
facies during exhumation based on a new geobarometer (8).
1. Okay, A.I., Xu Shutong & A.M.C. Şengör, 1989, Coesite from the
Dabie Shan eclogites, central China.
European Journal of Mineralogy, 1, 595-598.
2. Xu, S.T., Okay, A.I., Ji, S.Y.,
Şengör, A.M.C., Su, W., Liu, Y.C. & Jiang, L.L., 1992, Diamond from
the Dabie Shan metamorphic rocks and its implication for tectonic setting. Science, 256, 80-82.
3. Okay, A.I. &
Şengör, A.M.C., 1992, Evidence for intracontinental thrust-related
exhumation of the ultra-high-pressure rocks in China. Geology, 20, 411-414.
4. Okay, A.I., Şengör, A.M.C. & Satır,
M., 1993, Tectonics of an ultra-high pressure metamorphic terrane:
the Dabie Shan/Tongbai Shan orogen,
China. Tectonics, 12, 1320-1334.
5. Okay, A.I., 1993,
Petrology of a diamond and coesite-bearing metamorphic terrain: Dabie Shan,
China. European Journal of Mineralogy ,
5, 659-675.
6. Okay, A.I., 1994, Sapphirine and
Ti-clinohumite in ultra-high-pressure garnet-pyroxenite and eclogite from Dabie
Shan, China. Contributions to Mineralogy
and Petrology, 116, 145-155.
7. Schertl, H-P. & Okay, A.I., 1994,
Coesite inclusion in dolomite in Dabie Shan, China: Petrological and
rheological significance. European
Journal of Mineralogy, 6, 995-1000.
8. Okay, A.I., 1995, Paragonite
eclogites from Dabie Shan, China: Reequilibration
during exhumation ?. Journal of
Metamorphic Geology, 13, 449-460.
Blueschists
in the Tavsanli Zone in northwest Turkey
One of the best preserved blueschists
belts in the world; no retrogression; very low P/T gradients preserved; a prime
example of a subducted continental crust
General introduction and tectonic
setting
Okay, A.I., 1989,
Alpine-Himalayan blueschists. Annual Reviews of the Earth and Planetary
Sciences, 17, 55-87.
Okay, A.I., 1986, High
pressure/low temperature metamorphic rocks of Turkey. In: Blueschists and Eclogites (ed. B.W. Evans and E.H. Brown), Geological
Society of America Memoir No. 164, 333-348.
Okay, A.I., 1984, Distribution and characteristics of
the northwest Turkish blueschists. In:
The Geological Evolution of the Eastern Mediterranean (ed. J.E. Dixon &
A.H.F. Robertson), Geological Society
Special Publication No. 17, 455-466.
Okay, A.I., 1985, Metamorphic
belts in northwest Anatolia (in Turkish). In: Ketin Symposium Book, Publication
of the Geological Society of Turkey, Ankara, 83-92.
Petrology and P-T paths
Unique
jadeite + chloritoid assemblages in the metapelites indicate one of the highest
P/T ratios (24 kbar at 430° ) and lowest geotherms (5° C/km)in the continental
crust (papers 4 and 6); a prograde
reaction associated with penetrative strain producing sodic amphibole during
subduction (2, 3); incipient
metamorphism and metasomatism in the accretionary complex (3); first example of partial prograde
aragonitization of micritic limestones
(7); phonolites in blueschist facies with jadeite-K-feldspar-lawsonite
assemblages utilised as jade (5); a jadeite-granitoid
of Ordovician age (8).
1. Okay, A.I., 1980. Mineralogy, petrology and phase relations of
glaucophane-lawsonite zone blueschists from the Tavşanlı region, northwest Turkey. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,
72, 243-255.
2. Okay, A.I., 1980, Lawsonite
zone blueschists and a sodic amphibole producing reaction in the
Tavşanlı region, northwest Turkey.
Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 75, 179-186.
3. Okay, A.I., 1982, Incipient
blueschist metamorphism and metasomatism in the Tavşanlı region,
northwest Turkey. Contributions to
Mineralogy and Petrology, 79, 361-367.
4. Okay A.I. & Kelley, S.P, 1994,
Tectonic setting, petrology and geochronology of jadeite + glaucophane and
chloritoid + glaucophane schists from northwest Turkey. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 12, 455-466.
5. Okay, A.I., 1997,
Jadeite-K-feldspar rocks and jadeitites from
northwest Turkey. Mineralogical
Magazine, 61, 835-843.
6. Okay, A.I., 2002, Jadeite-chloritoid-glaucophane-lawsonite
schists from northwest Turkey: unusually high P/T ratios in continental
crust. Journal of Metamorphic Geology,
20, 757-768.
7. Topuz, G., Okay, A.I., Altherr, R., Meyer, H.P. & Nasdala,
L., 2006, Partial high-pressure aragonitization of
micritic limestones in an accretionary complex,
Tavşanlı Zone, NW Turkey.
Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 24, 603-613.
Exhumation and associated Eocene
magmatism
Constraints
on the exhumation of the subducted continental upper crust and a mechanism for
exhumation (11); origin of the Eocene plutons
intruding the blueschists and the overlying ophiolites (12, 14).
1. Okay, A.I., Harris, N.B.W. & Kelley,
S.P., 1998, Exhumation of blueschists along a Tethyan suture in northwest
Turkey. Tectonophysics, 285, 275-299.
2. Harris, N.B.W., Kelley, S. &
Okay, A.I., 1994, Post-collision magmatism and tectonics in northwest
Anatolia. Contributions to Mineralogy
and Petrology, 117, 241-252.
3. Akyüz, H.S. & Okay, A.I., 1999, The geology of the south of
Manyas (Balıkesir) and
the tectonic significance of blueschists.
Bulletin of the Mineral Research and Exploration, 120, 81-95.
4. Okay, A.I. & Satır,
M., 2006, Geochronology of Eocene plutonism and metamorphism in northwest
Turkey: evidence for a possible magmatic arc.
Geodinamica Acta,
19, 251-266.
5. Sunal, G., Erturaç,
M.K., Topuz, G., Okay, A.I. & Zack, T., 2019, The Early Eocene Ekmekçi Granodiorite porphyry in
the Karacabey region (western Sakarya Zone), NW
Turkey. Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 28, 589-602.
Geochronology
Ar-Ar
and Rb-Sr phengite and sodic amphibole data for the Late Cretaceous (80 Ma)
HP/LT metamorphism (1, 2); zircon Pb-Pb data on the Triassic and Ordovician
protolith ages.
1. Sherlock, S., Kelley, S.P., Inger,
S., Harris N. & Okay, A.I., 1999, 40Ar-39Ar and Rb-Sr
geochronology of high-pressure metamorphism and exhumation history of the
Tavsanli Zone, NW Turkey. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 137,
46-58.
2. Okay A.I. & Kelley,
S.P, 1994, Tectonic setting, petrology and geochronology of jadeite +
glaucophane and chloritoid + glaucophane schists from northwest Turkey. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 12, 455-466.
Modelling
Bodur, Ö. F., Göğüş,
O. H., Pysklywec, R. N., & Okay, A. I. (2018).
Mantle lithosphere rheology, vertical tectonics, and the exhumation of (U)HP
rocks. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 123, 18241839.
HP/LT
rocks from other parts of Turkey
Triassic
blueschists and eclogites related to the Paleo-Tethyan subduction
Okay, A.I. & Monié, P., 1997, Early Mesozoic subduction in the Eastern
Mediterranean: Evidence from Triassic eclogite in northwest Turkey. Geology, 25, 595-598.
Okay, A.I., Monod, O. & Monié, P., 2002, Triassic blueschists and eclogites from
northwest Turkey: vestiges of the Paleo-Tethyan subduction. Lithos, 64, 155-178.
A thin eclogite nappe in the Alanya Massif, Taurides
Okay, A.I. & Özgül, N., 1984, HP/LT metamorphism
and the structure of the Alanya Massif, Southern
Turkey: an allochthonous composite tectonic sheet. In: The Geological Evolution of the Eastern
Mediterranean (ed. J.E. Dixon &
A.H.F. Robertson), Geological Society Special Publication No. 17, 429-439.
Okay. A.I., 1989, An exotic
eclogite/blueschist slice in a Barrovian-style
metamorphic terrain, Alanya Nappes, southern Turkey.
Journal of Petrology, 30, 107-132.
Çetinkaplan, M., Pourteau,
A., Candan, O., Koralay, O.E., Oberhänsli,
R., Okay, A.I., Chen, F., Kozlu, H. & Şengün, F., 2016, P-T-t evolution of eclogite/blueschist
facies metamorphism in Alanya Massif: time and space
relations with HP event in Bitlis Massif, Turkey. International Journal of
Earth Sciences, 105, 247281.
Precambrian
kyanite-eclogites from the Bitlis Massif, southeast Anatolia
Okay, A.I., Arman, M.B. &
Göncüoğlu, M.C., 1985, Petrology and phase relations of the
kyanite-eclogites from eastern Turkey.
Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 91, 196-204.
Early
Cretaceous blueschists and eclogites from the central Pontides
Okay, A.I., Tüysüz, O., Satır, M., Özkan-Altıner,
S., Altıner, D., Sherlock, S., & Eren, R.H.,
2006, Cretaceous and Triassic subduction-accretion, HP/LT metamorphism and
continental growth in the Central Pontides, Turkey. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 118,
1247-1269.
Rhodopian eclogites from
northwest Turkey
Okay, A.I. & Satır, M., 2000, Coeval plutonism and metamorphism in
a latest Oligocene metamorphic core complex in northwest Turkey. Geological Magazine, 137, 495-516.
Okay, A.I. & Satır, M., 2000, Upper
Cretaceous eclogite facies metamorphic rocks from the Biga
Peninsula, northwest Turkey. Turkish
Journal of Earth Sciences, 9, 47-56.
Enigmatic
blueschists from Thrace
Şentürk, K. & Okay, A.I., 1984,
Blueschists discovered east of Saros Bay in Thrace. Bulletin of the Mineral Research and Exploration Institute of Turkey, 97/98,
72-75.
Topuz, G., Okay, A.I.,
Altherr, R., Satir, M., Schwarz, W.H., 2008, Late
Cretaceous blueschist-facies metamorphism in southeastern Thrace (Turkey) and
its geodynamic implications. Journal
of Metamorphic Geology, 26, 895913.
None
HP/LT metamorphic rocks from Turkey
Okay, A.I., 1984, The geology
of the Ağvanis metamorphic rocks and neighbouring formations.
Bulletin of the Mineral Research and Exploration Institute of Turkey,
99/100, 16-36.
Okay, A.I., 1996, Granulite
facies gneisses from the Pulur region, Eastern Pontides. Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 5, 55-61.
Okay, A.I. & Satır, M., 2000, Coeval plutonism and metamorphism in
a latest Oligocene metamorphic core complex in northwest Turkey. Geological Magazine, 137, 495-516.
Mineralogy
A novel method of estimating oxygen fugacities (partial pressures) in sodic amphibole bearing
rocks (3,4); changes in the composition of sodic pyroxenes with increasing
grade (1), lawsonite, a major blueschist mineral its importance (6) and
composition (5).
1. Okay, A.I., 1978. Sodic pyroxenes
from metabasites in the eastern Mediterranean.
Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 68, 7-11.
2. Carpenter, M.A. & Okay, A.I.,
1978. Topotactic replacement of augite
by omphacite in a blueschist rock from northwest Turkey. Mineralogical Magazine, 42, 435-438.
3. Okay. A.I., 1980,
Sodic amphiboles as oxygen fugacity indicators in metamorphism. Journal of
Geology, 88, 225-232.
4. Okay, A.I., 1987,
The oxygen fugacity stability of deerite: an
alternative view. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 5, 553-555.
5. Sherlock, S.C. & Okay, A.I.,
1999, Oscillatory zoned chrome lawsonite in the Tavsanli Zone, northwest
Turkey. Mineralogical Magazine, 63,
687-692.
6. Whitney, D.L., Fornash, K.F., Kang, P., Ghent, E.D., Martin, L., Okay,
A.I. & Brovarone, A.V., 2020, Lawsonite
composition and zoning as tracers of subduction processes: a global review. Lithos, 370371, article 105636.
Misc
Gökçeoğlu, C., Okay, A.I.
& Sezer, E., 2008, International earth science literature from Turkey
1970-2005: trends and possible causes. Scientometrics, 74, 409-423.
Okay, A.I.,
Altıner, D. & Less, G., 2023, Obituary - Prof. Dr. Ercan Özcan. Turkish
Journal of Earth Sciences,
32, 145-148.
Choi, S.;
Fabbri, O.; Topuz, G., Okay, A.I. & Jung, H., 2021, Twin induced reduction of seismic anisotropy in lawsonite
blueschist. Minerals, 11, 399.
Aygül, M.,
Okay, A.I., Hacker, B., & Kylander-Clark, A.R.C.,
2022, REE behavior in warm and cold subducting
oceanic crust.
International Journal of Earth Sciences,
111, 905918.
