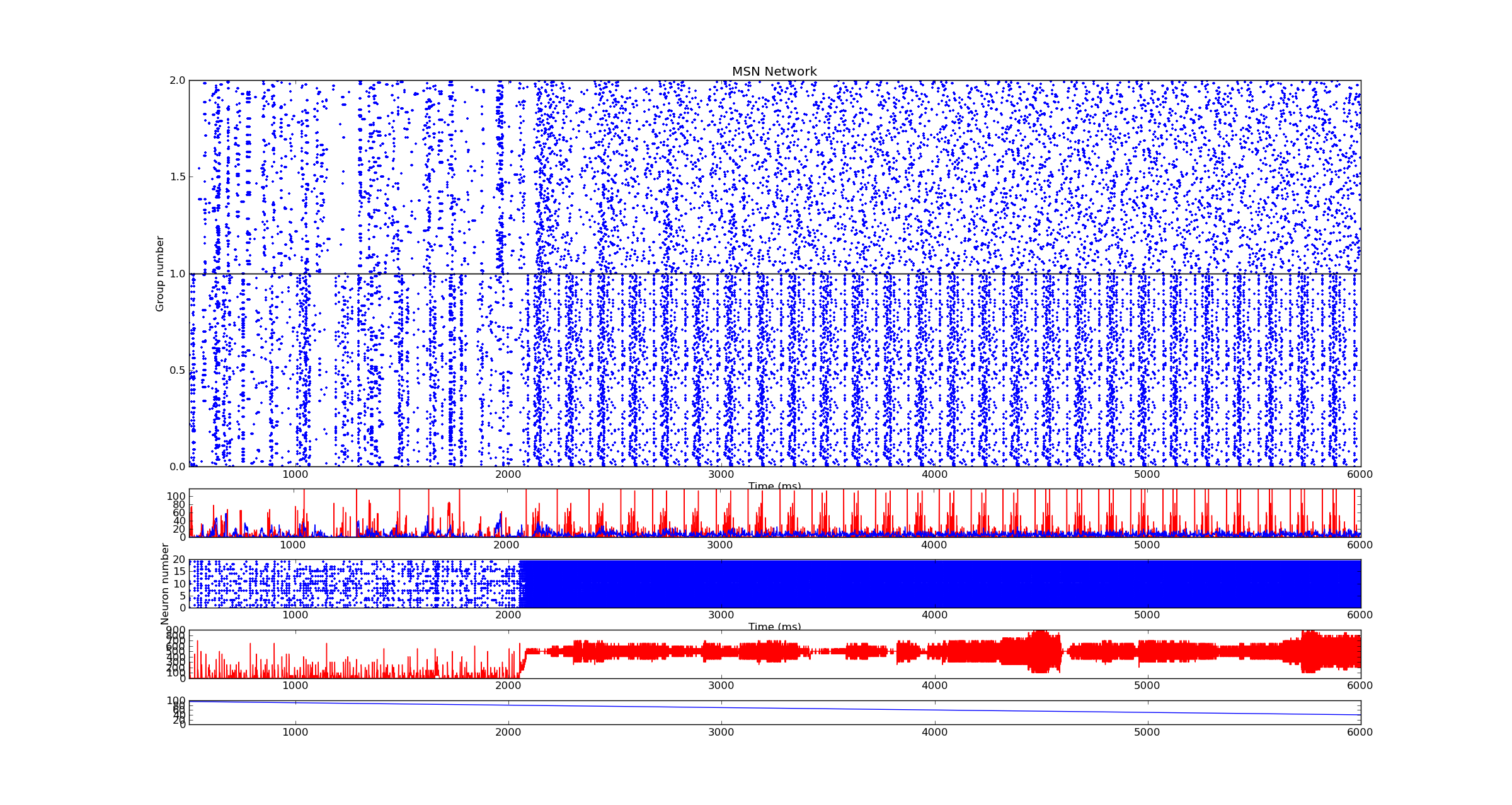
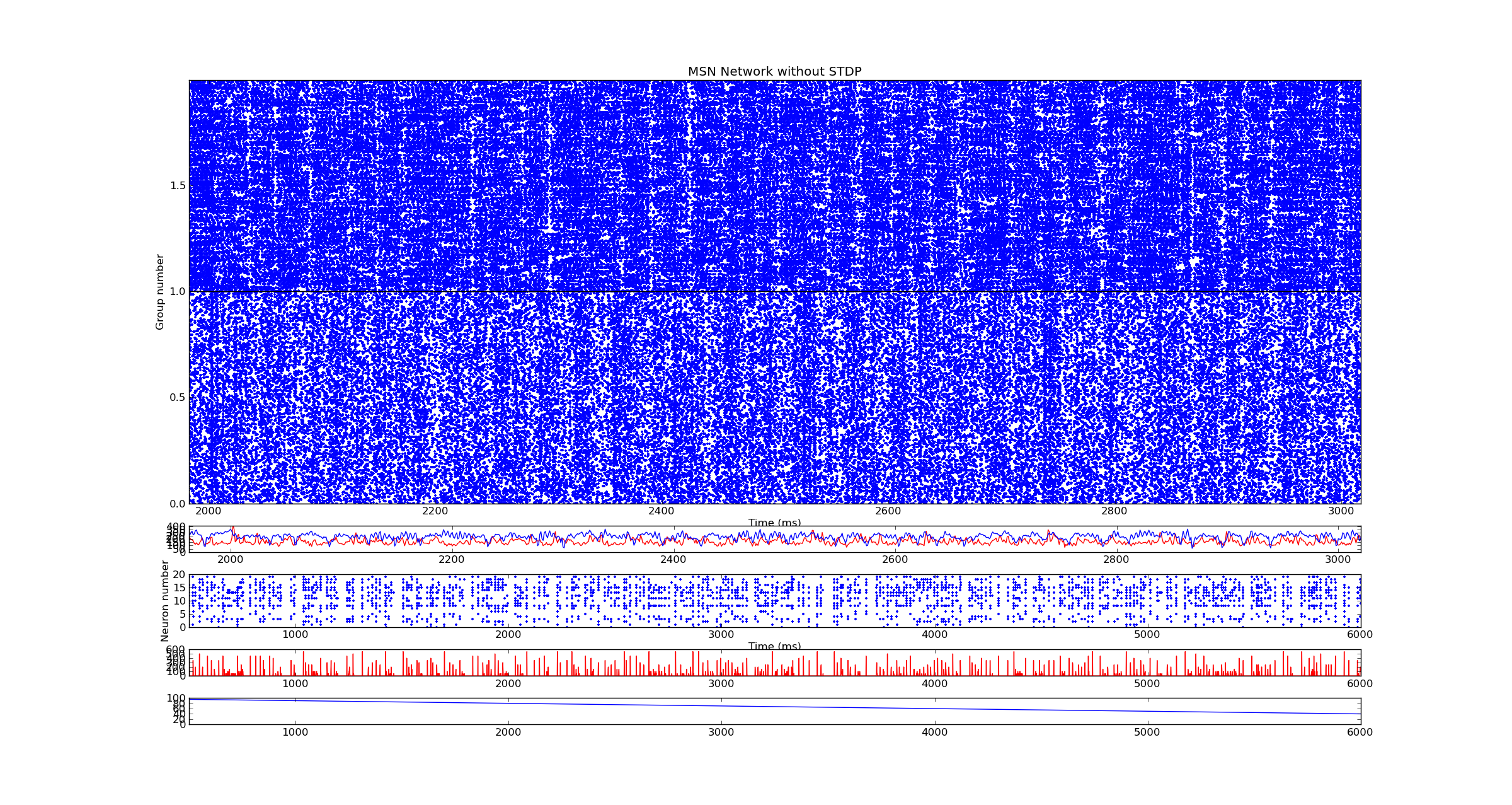
Medium Spiny Neurons
The role of basal ganglia in motor control is well-known, but it also takes part in high order cognitive processes, such as reward-related learning, goal-directed behavior or selective attention. The complicated and creative information processing ability of basal ganglia makes it home for decisions amongst available competitive choices. Dysfunction of this sub-cortical network, along with the related neurotransmitters (e.g. dopamine), causes neurodegenerative diseases as Parkinson's Disease or Huntington's Disease. D1 and D2 type dopamine receptors have a modulatory effect on this network by controlling the GABAergic signalling from the basal ganglia main input station, striatum, to the direct and indirect pathways. The striatal medium spiny neurons (MSNs) play key role in the formation of the antagonistic functions of direct and indirect pathways. We focused on the state-space behavior of the conductance-based computational model of MSNs which is constituted with nonlinear dynamical systems' approach.
How pathological synchronous patterns occur within striatum?
A. with STDP? B. without STDP?
A. with STDP? B. without STDP?