|
Mechanistic transformation, in which a polymer obtained by a certain polymerization mechanism is functionalized either by initiation or termination steps for the initiation of another polymerization mechanism, has been proposed to extend the range of monomers for the synthesis of block copolymers. This approach also provides a straightforward route to obtain block copolymers that cannot be made by a single polymerization mode. The methodology depends on isolation and purification of the first polymer segment and finally, convertion of the the functional groups into another kind of species capable of initiating the polymerization of the second monomer. Combinations of very wide range of polymerization techniques have been studied and reviewed. Today, the combination (i. e. transformation) of two different polymerization mechanisms is a well-accepted route to synthesize block copolymers.
According to the functionalization procedure, transformation reactions can be classified in three ways. These are: (i) functionalization of initiator (utilization of dual initiator), (ii) termination functionalization by polarity inversion and (iii) termination functionalization by an initiator.
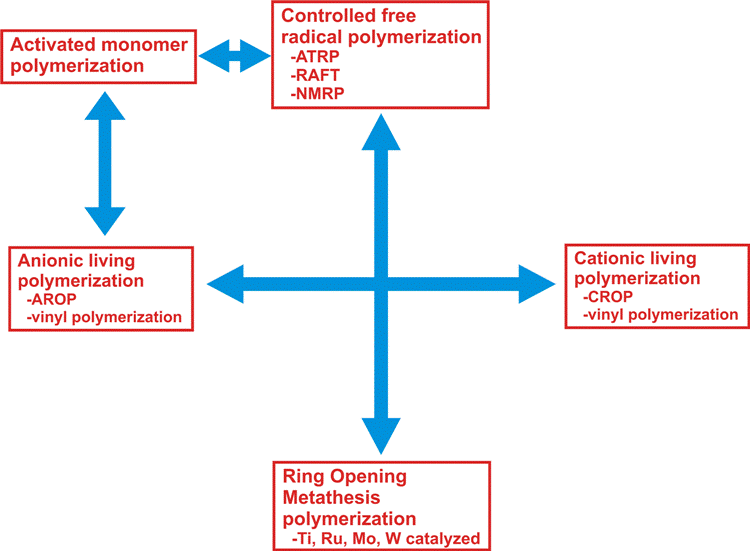
On the Other hand, transformation reactions can mechanistically be classified on the basis of interconversion between propagation mechanisms (See Figure below). Accessibility of transformation mechanisms in both directions allows one to design different strategies to synthesize block copolymers. Rest of the chapter is devoted to such interconversion mechanisms.