Airfoil Nomenclature¶
An airfoil is the cross section of a wing or a blade in spanwise direction. When exposed to a freestream, aerodynamic forces and moments are created on the airfoil. The analysis of 2D airfoils provide important information about the wing/blade properties. Different types of airfoils are used for different types of flows. Although there are numeruos types and shapes for airfoils, the nomenclature is same. An airfoil can be thouht as a combination of two surfaces; upper and lower surface, then
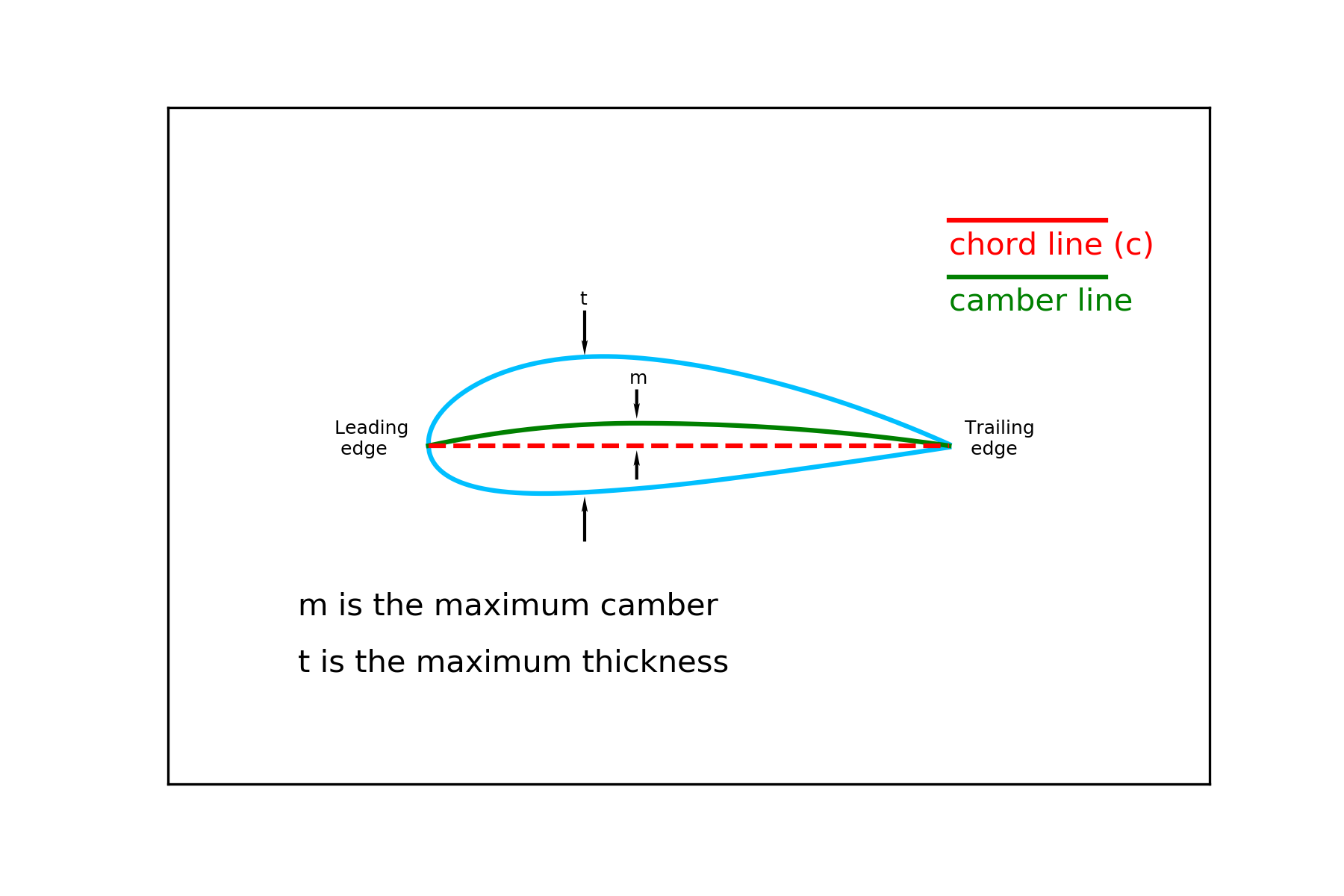
- The point that these surfaces are joined and facing the freestream is called the leading edge (LE) and the other connection point at the rear is called the trailing edge (TE).
- The straight line that connects the leading edge and the trailing edge is the chord line and denoted by $c$.
- The camber line connects the points that are in the halfway from the upper to lower surface.
- The camber is the distance between the chord line and the camber line.
- Thickhness is the distance between the upper and lower surfaces along the chord.
<< 2.4 Conservation of Energy || Contents || 3.1.1 NACA 4 Digit Airfoils >>
References:
[1] Summary of Airfoil Data, I.H. Abbott, A.E. von Doenhoff, L.S. Stevers, Jr, NACA Report No. 824, 1945.
[2] www.airfoiltools.com