|
EHB 222E Introduction
to Electronics (CRN: 22984) Grading: Midterm Exams 2x 30%, Final
Exam 40% SPRING BREAK 2-6 MAY 2022
I created a Ninova page for your section.
You can access it using your ITU student account and password. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Course Description: |
·
Semi-conductor
basics: concepts and semi-conductor components. ·
Semiconductor diode; physical
structure, terminal characteristics, analysis of diode circuits. ·
Bipolar junction transistor (BJT);
physical structure and operating modes, BJT as a switch; DC biasing, BJT as
an amplifier, small-signal model, basic amplifier circuits. ·
MOSFET; structure and operating
modes, MOSFET as a switch, MOSFET amplifiers. ·
Operational
amplifiers; concepts and application examples. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Önemli Kurallar/Important Rules: |
Sınavlarda hesapladığınız akım ve gerilimlerin yönlerini çözüm kağıdı üzerinde belirtiniz. Kağıdınızı okuyan kişi sınav
sırasında aklınızdan geçen herşeyi kestirebilecek güçte olmadığı için, anlayamadığı hesaplara not veremez. Yarıyıl içi ve yarıyıl sonu
sınavlarında her öğrencinin
A4 boyutlu bir "kopya kağıdı" kullanma hakkı vardır. Arkalı önlü olarak hazırlanabilecek
olan bu kağıda öğrenci sınav için gerekli
olduğuna inandığı herşeyi yazmakta serbesttir; ANCAK, "kopya kağıdı"
bilgisayar çıktısı veya fotokopi yöntemi ile çoğaltılamaz,
her öğrenci kendi "kopya kağıdı"nı kendi el yazısı ile hazırlar. Sınav sonunda kağıtlar toplanırken "kopya kağıt"ları da sınav kağıtları ile beraber toplanır.
Yararlanıldığı halde
"kopya kağıdı" olmayan sınav kağıdının puanı düşürülecektir. Benzer biçimde, sınav sırasında ders notları, defter veya çözümlü problemler kullanılmaz; böyle bir girişimde
bulunan öğrencinin sınav kağıdının puanı düşürülecektir. Sınavlara gerçek hesap makinesi ile geliniz, her ne için olursa olsun
cep telefonlarını kullanmanıza
izin verilmeyecek, cep telefonları sınav sırasında kapalı kapalı tutulacak ve ASLA kullanılmayacaktır. Kullanma girişiminde bulunanlar cezalandırılacaktır. During
midterm and final exams each student may bring and use an A4 size "copy
sheet". This double sided hand prepared copy sheet may contain all
formulae the student thinks is important for solving exam problems. HOWEVER, the "copy
sheet" MAY NOT be a printout or photocopy of someone else's. At the end
of the exam period the copy sheet should be turned in along with problem
solutions. No class
notes or problem solutions may be used during the exam; anyone attempting to
use such material will be penalized. You may
only use a real calculator during the exam, cell phones are not allowed, and
should be turned off. Anyone attempting to use his/her cellphone(s) will be
strictly penalized. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Textbooks: |
Unfortunately, Semiconductor Electronics is not well covered in both of these books above. Thus
are recommended. Have a look at online
library resources such as CRC ENGnetBASE. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Course Plan
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Simulation Tools:
|
SPICE can be downloaded from
Linear Technology website.
ABACUS by nanoHUB.
|
|
Interesting Links:
|
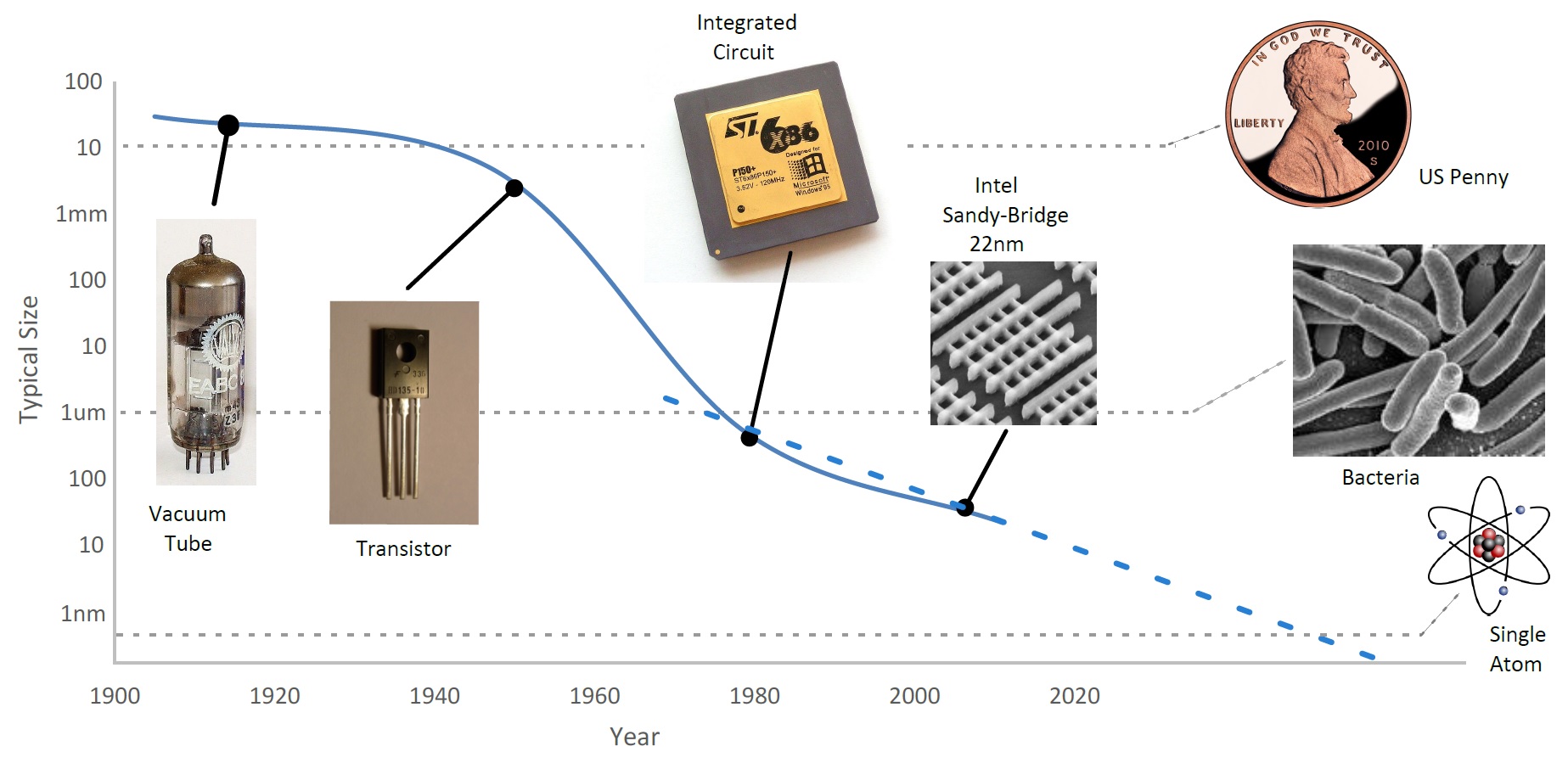
A single-atom transistor (Nature Nanotechnology Jan 2012)
How We Found the Missing Memristor (IEEE Dec 2008)
|
|
|
|